

In contrast Group 7 elements you will find (I will draw an example) it's easier to gain electrons from surroundings because their outer ring is nearly full, so they'll have more electrons than protons and therefore become negatively charged in their ionic state e.g. When writing the symbol for an ion, the one- or two-letter element symbol is written first, followed by a superscript. Looking at the table, one can see that the positive. This therefore means there's one less electron than there are protons hence Na+ charge in it's ionic form. An elements placement on the periodic table indicates whether its chemical charge is negative or positive.
#IONIC CHARGE PERIODIC TABLE FULL#
Atoms like having full rings, so it's just easy if Na 'kicks' out that one electron becoming 2 + 8. See that the outer ring only has 1 electron. (DRAW OUT Na STRUCTURE) - 2 + 8 + 1 = 11. The inner ring only holds 2 all subsequent rings hold 8. As you can see from the partial table shown above the Groups of the periodic table each form a unique charge of ion. For example, iron(II) has a 2+ charge iron(III) a 3+ charge. Group 1A and 2A of the periodic table, alkali metals and alkaline. Ions form naturally based on where they are located in the periodic table. Cations Ionic Charges Chart (Cations and Anions) Roman numeral notation indicates charge of ion when element commonly forms more than one ion. Remember protons and neutrons are in the nucleus electrons orbit it in rings. Whether an atom forms a cation or an anion depends on its position on the periodic table. Up there when we talked about boron being negative, a negative ion, that is an anion. The general term when we're talking about a positive ion, we're talking about a cation. This is a platinum ion, a positive platinum ion.
#IONIC CHARGE PERIODIC TABLE PLUS#
Na which has an atomic number of 11 (number of protons and therefore electrons - if both are equal it's a neutral charge). So you could write this as platinum with a plus four charge. (n)- means the opposite. Look at the elements on the periodic table e.g. (n)+ means there're more protons (positively charged) than electrons (negatively charged).
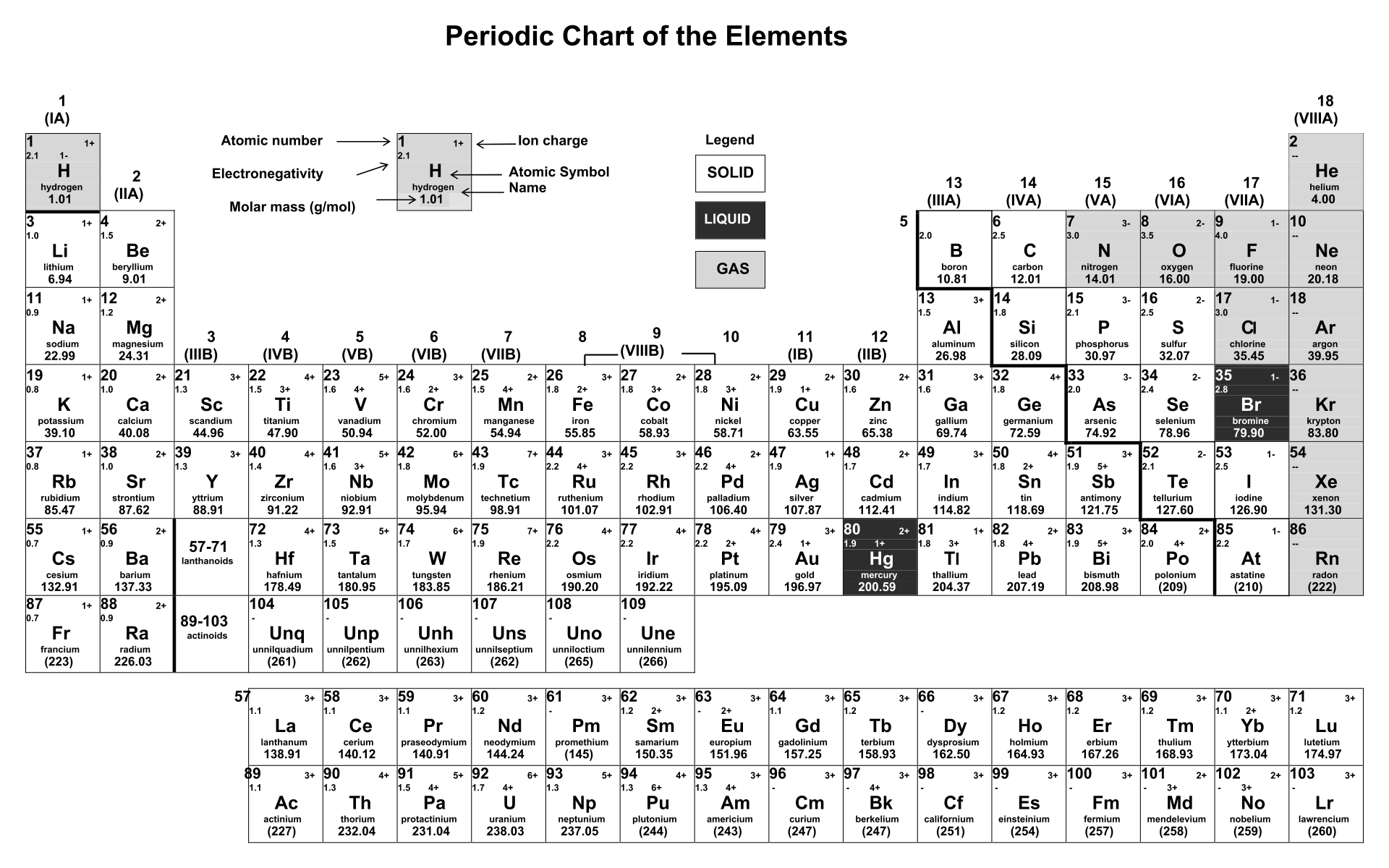
Group 1 elements become 1+, Group 2 becomes 2+, Group 3 becomes 3+, Group 4 becomes 4+, Group 5 becomes 3-, Group 6 becomes 2-, Group 7 becomes 1-, Group 8 is always 0 (inert). The useful thing is that different elements have been grouped together on the periodic table so that it's easy to see which ones share something in common.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
